3D Spatial Audio
3D Spatial Audio brings the real-world sound experience to the virtual world, providing an immersive audio experience for users. Agora's spatial audio technology enables you to simulate the propagation characteristics of sound in a physical environment within a virtual interactive scene.
-
Ultra-realistic space shaping effect
Utilize technologies such as range audio, sound blur, and air attenuation simulation to perfectly simulate the real auditory experience.
- Set the spatial positions of users in real time to give a sense of change in the distance, direction, and orientation of other users.
- Update the spatial position of the media player, to add a sense of space to background sounds, accompaniments, and other media resources.
- Add 3D Spatial Audio effects such as sound blurring and air attenuation by adjusting audio settings to perfectly simulate the real audio experience.
-
3D High Fidelity
- Sound effects are processed and rendered based on the facial orientation, sound source orientation, and relative position of the sound source in 3D space.
- Supports 48 kHz full-band sampling and 3D high-fidelity audio processing and rendering.
-
Multi-platform support
Supports iOS, Android, macOS, Windows, Web, Unity, Flutter, React Native, Electron, Unreal and other platforms.
-
Ultra-low latency, low power consumption, and low cost
The spatial audio algorithm adopts an advanced front-end processing mode and synchronizes spatial coordinates through cloud services. The end-cloud collaborative processing mode effectively reduces overall latency and power consumption.
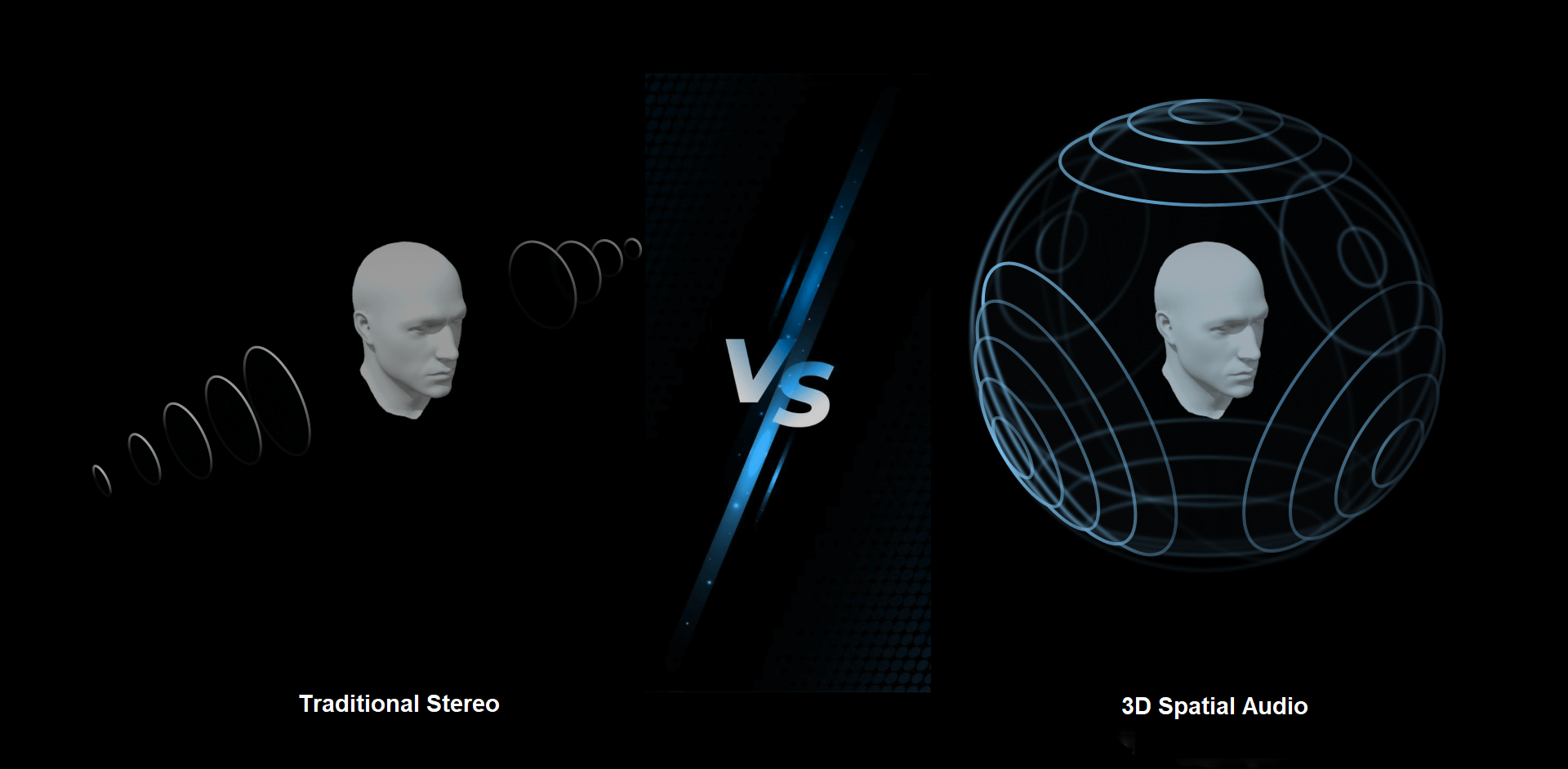
Compared to traditional stereo, which relies on left and right channels, spatial audio technology greatly enhances the depth and realism of sound. The following table highlights these enhancements:
| Feature | Traditional Stereo | Agora Spatial Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Dimensionality | Left and right dimensions | Represents sound in a full 3D space using the x, y, and z axes of the world coordinate system, corresponding to right, top, and front dimensions |
| Spatial Perception | Adjust the volume of the left and right channels to create a spatial sound | Utilizes advanced spatial audio algorithms to create a realistic soundscape by manipulating parameters like distance, direction, and orientation |
| User Experience | Flat | Immersive, three-dimensional, and natural, delivering a realistic auditory experience |
Applicable scenarios
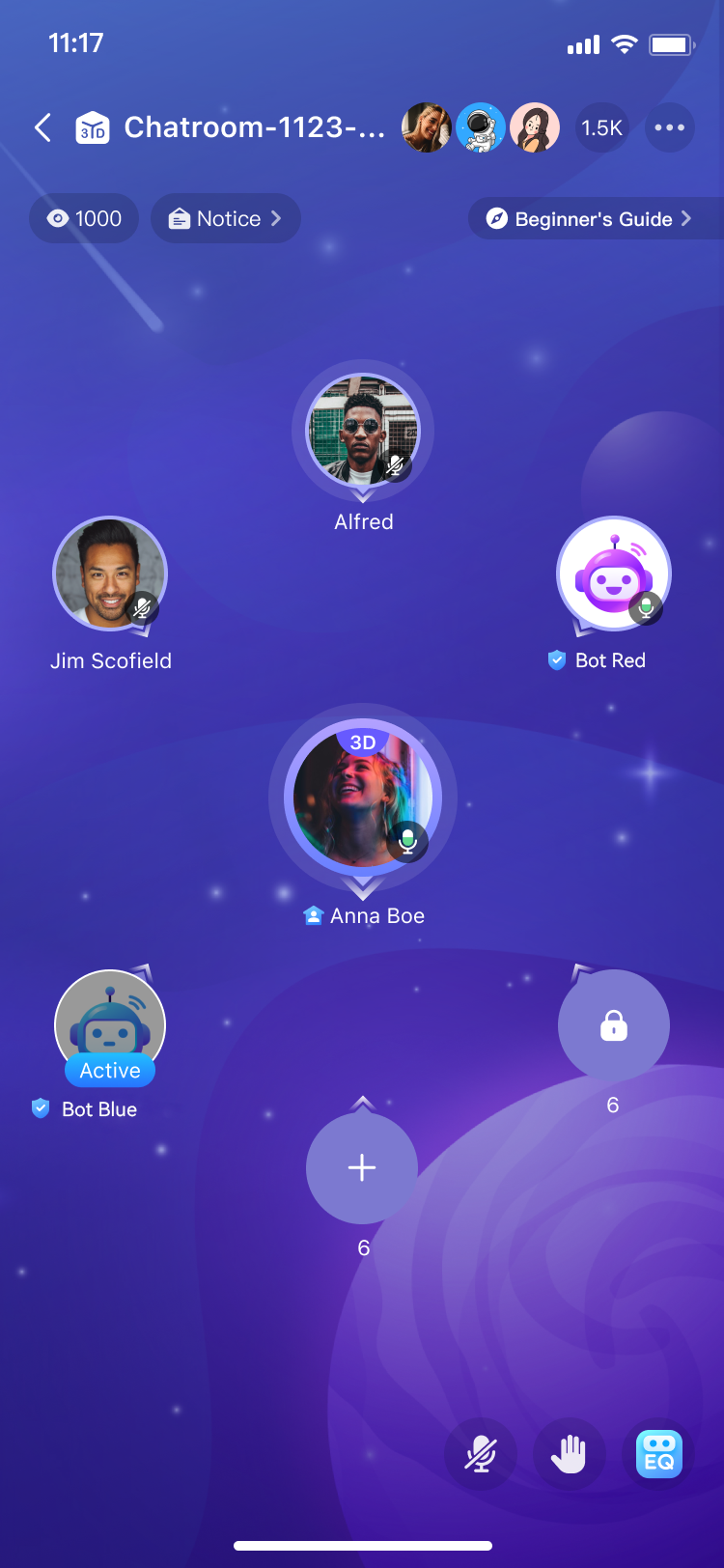
Social Chat
In the Voice Chat Room app, user avatars are arranged in a grid, each assigned specific coordinates and a direction. During interaction, the volume and direction of each user's voice correspond to their location. As you drag your avatar across the screen, the volume of another user decreases as you move away and disappears when you exceed a certain distance, simulating real-world sound propagation.
Games & Metaverse
In 3D environments like games and the Metaverse, spatial audio technology can enhance experiences in the following ways:
| Audio Blurring | Enable audio blurring for specific users or media. For example, in a coffee shop, use this to create a "whispering" effect where other users hear muffled conversations. |
| Range Audio | Set audio reception range based on the scene. The farther the sound travels, the fainter it becomes. Adjust the attenuation factor for different effects:
|
| Ultra-Realistic Space | Assign virtual characters 3D coordinates for a realistic spatial experience, including:
|
| Sound Insulation Area | Create sound-insulated zones with customized sound attenuation. When a receiver outside the area listens to the sound source in the area, they experience the attenuation effect of the sound in the real environment on encountering the building partition. For example, in a KTV scene, sounds from inside a box can be faintly heard from outside. Opening the door instantly amplifies the sound. |

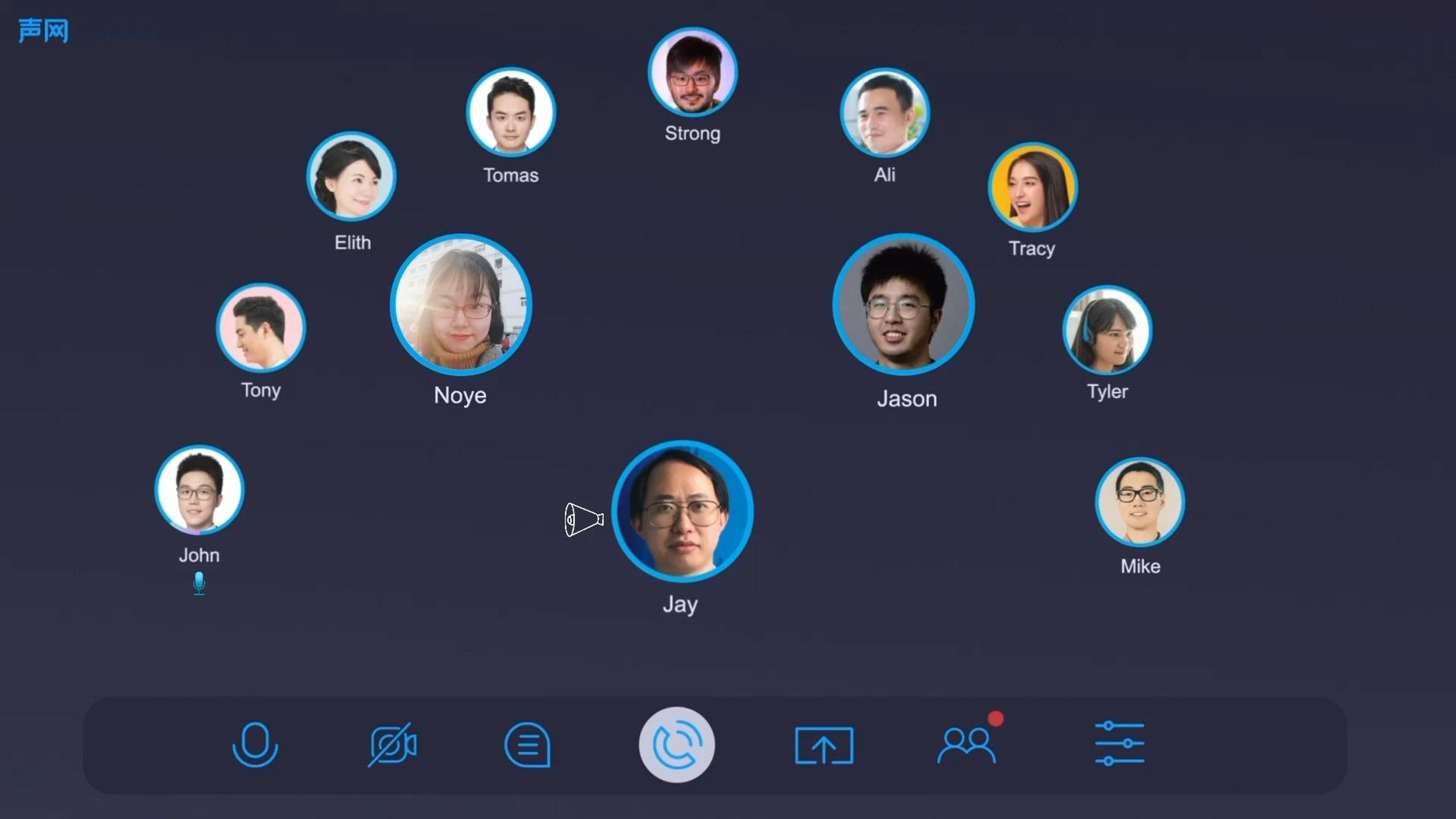
Online Meetings
In virtual meetings, spatial audio can arrange users around the host, with each microphone having directional sound. This setup mimics a real-world conference room, providing a more immersive and less tiring experience compared to traditional online meetings.
This page shows you how to implement 3D Spatial Audio in your app.
Understand the tech
Agora provides a local Cartesian coordinate system calculation scheme for setting up 3D Spatial Audio positions for users and the media player.
3D Spatial Audio for users
Use an instance of ILocalSpatialAudioEngine to implement 3D Spatial Audio. Call updateSelfPosition and updateRemotePosition to specify the spatial coordinates of local and remote users in the channel. Voice SDK calculates the relative positions of local and remote users. This enables local users to experience the 3D Spatial Audio of remote users.
3D Spatial Audio for media player
Call updateSelfPosition and updatePlayerPositionInfo methods of the ILocalSpatialAudioEngine class to update the spatial coordinates of local users and the media player. The SDK calculates the relative positions of local users and the media player. This enables local users to experience the 3D Spatial Audio effect of the media player.
Prerequisites
Ensure that you have implemented the SDK quickstart in your project.
Implement 3D Spatial Audio
The following figure shows the workflow you implement to provide 3D Spatial Audio for users and the media player:
Initialize the spatial audio engine
Call the create method of the ILocalSpatialAudioEngine class to create an instance of the spatial audio engine. Then, call initialize to enable spatial audio.
Set the audio profile and scenario
To set the desired audio encoding properties, call setAudioProfile.
Call setAudioScenario to set the scenario to AUDIO_SCENARIO_GAME_STREAMING for the best sound quality effect.
Set the audio reception range
To set the maximum number of audio streams that can be received within the audio receiving range, call setMaxAudioRecvCount. The recommended maxCount value is ≤ 16.
To set the maximum range of receivable audio, in meters, call setAudioRecvRange. The recommended value range is > 0.
Update spatial position
In the user space audio scenario, call the updateSelfPosition and updateRemotePosition methods to update the positions of the local user and remote users respectively.
In the media player spatial audio scenario, call the updateSelfPosition and updatePlayerPositionInfo methods to update the position of the local user and the media player, respectively.
Typically, you call these methods when:
- A new user joins the channel.
- The relative positions of the local user, a remote user, or the media player changes.
- There are other changes in your specific scenario.
Set spatial audio parameters
To set spatial audio parameters for the remote user or media player, call setRemoteUserSpatialAudioParams or setSpatialAudioParams. To implement specific sound effects, refer to the following parameter settings:
-
Air attenuation effect
Set
enable_air_absorbtotrueand setspeaker_attenuationto the desired sound attenuation coefficient. -
Sound blur effect
Set
enable_blurtotrue
Set up sound isolation (optional)
To define a sound isolation zone and set a sound attenuation coefficient call setZones. This feature simulates the real-world effect of sound attenuation when the sound source is inside a sound isolation zone while the receiver is outside or vice versa. It mimics how sound behaves when encountering obstacles like building partitions.
Optionally, call setRemoteAudioAttenuation or setPlayerAttenuation to set the sound attenuation properties for the user and media player, respectively, and specify whether to use this setting to forcefully override the sound attenuation factor in setZones.
Set headphone equalization (optional)
To optimize the audio experience, call setHeadphoneEQPreset to choose a preset headphone equalizer.
If the preset values do not provide the desired effect, call setHeadphoneEQParameters to self-adjust headphone equalization. After you execute this method, the preset values set by setHeadphoneEQPreset are overwritten.
Pause or turn off spatial audio
During a session, pause or turn off spatial audio as follows.
Pause spatial audio for a remote user
To disable a remote user's spatial audio, or to remove a remote user who has exited the channel, call removeRemotePosition to delete the user's spatial position information and save computing resources.
When a remote user leaves the channel, call removeRemotePosition to delete the user's spatial position information. Otherwise, the local user may not be able to hear the spatial audio from other remote users.
To restore the user's spatial audio, call updateRemotePosition to reset the remote user's position information.
Pause spatial audio for all remote users
If you do not want to continue to experience local spatial audio, call clearRemotePositions to delete the spatial position information of all remote users.
Calling this method prevents the local user from hearing the audio of all remote users. Agora recommends using this method with caution.
To resume hearing the remote user's audio later, call muteAllRemoteAudioStreams(false) to subscribe to the remote audio streams again.
Pause the local user's spatial audio
To unpublish the local audio stream, call muteLocalAudioStream(true).
To enable spatial audio again, call the same method with the parameter set to false.
Turn off spatial audio
To turn off spatial audio, call the enableSpatialAudio method of the RtcEngine instance and set the parameter to false. This resets all settings related to spatial audio.
To enable spatial audio again, call this method again and set the parameter to true, and then call the relevant APIs again to set the spatial audio effect.
Call the destroy method of the ILocalSpatialAudioEngine class to free up resources.
Reference
This section contains content that completes the information on this page, or points you to documentation that explains other aspects to this product.
Sample project
Agora provides the SpatialSound open-source sample project for your reference. Download the project or view the source code for a more detailed example.


