REST quickstart
Real-Time STT subscribes to the audio content of a media stream and transcribes it into text in real time. This page shows you how to use basic RESTful API to enable Real-Time STT.
Note that the command-line examples are for demonstration purposes only. In a production environment, send RESTful API requests through your application server.
Understand the tech
The following diagram illustrates the complete process of implementing Real-Time STT:
This includes the following steps:
-
acquireBefore starting the transcription, call
acquireto obtain a transcription resource. If the request is successful, you get a resource ID in the response body. -
startCall
startto join the channel and start the transcription. If the request is successful, you get a task ID in the response body that marks the current transcription session. -
updateWhen Real-Time STT is enabled, the
updatecommand can support changing some parameters like language or whether to transcribe for a specific host or all hosts in a channel. -
queryBetween the
startandstopcalls, you can query the service status and update configuration parameters. -
stopCall
stopto stop the transcription.
Prerequisites
To follow this procedure, you must:
-
Have a valid Agora Account.
-
Have a valid Agora project with an app ID and a temporary token or a token server. For details, see Agora account management.
-
Have a computer with access to the internet. If your network has a firewall, follow the steps in Firewall requirements.
-
Join a Video SDK channel as a host and start streaming. Refer to the Voice SDK quickstart guide.
Project setup
To enable Real-Time STT before using it for the first time, take the following steps:
- Log in to Agora Console and open the Project Management page.
- Find the project for which you want to enable Real-Time STT and click the pencil icon.
- On the Edit Project page, find Real-Time STT and click Enable.
- Click Enable Real-Time STT and Apply to confirm.
Now you can use Agora Real-Time STT and see the usage statistics on the Usage page.
Implement Real-Time STT
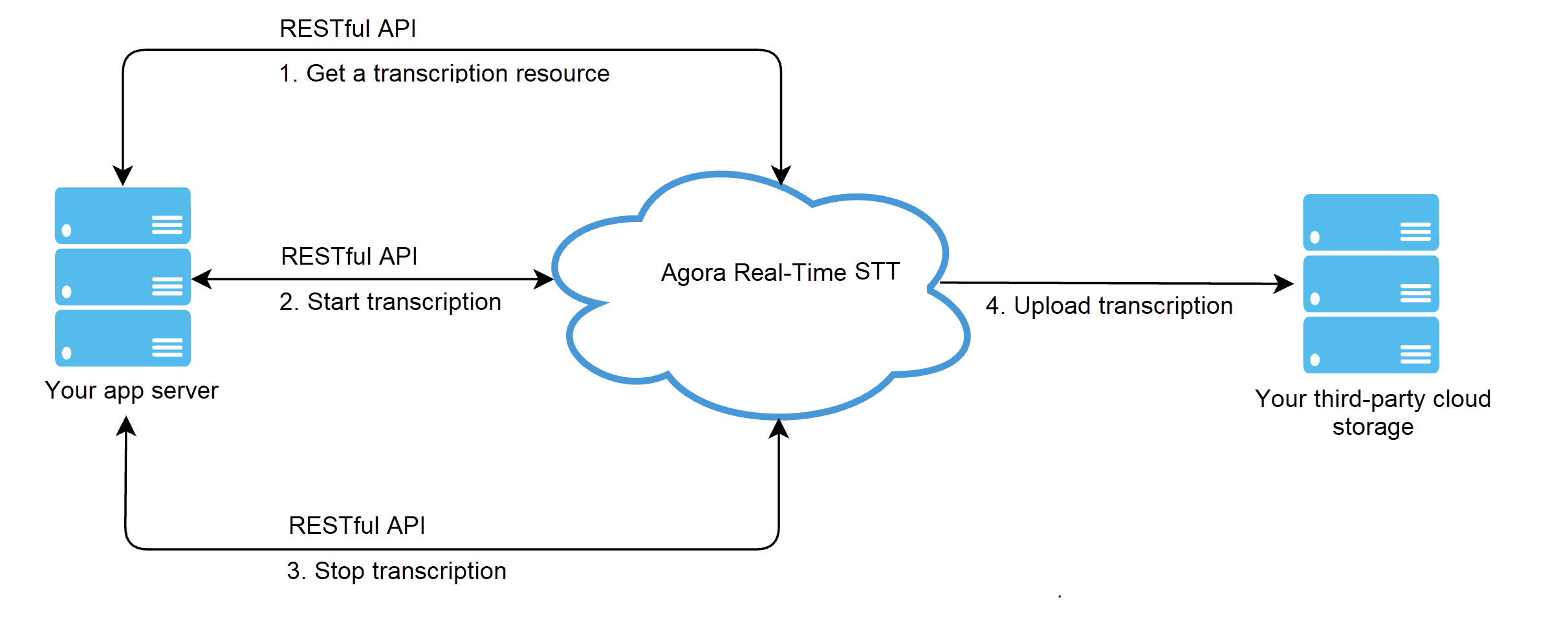
The following diagram shows a simple API call sequence of Real-Time STT, including querying the status and updating the configuration before the transcription stops:
Pass basic HTTP authentication
RESTful APIs require you to pass basic HTTP authentication by setting the Authorization parameter in every HTTP request header. For how to get the Authorization value, see RESTful authentication.
Acquire a token and reserve a resource
Call acquire to request buildToken and reserve a resource for Real-Time STT.
After a successful request, you get tokenName, also referred to as a resource ID, in the response body. The resource ID is valid for five minutes only, so you need to start transcribing within that time. Because the stop request also requires the resource ID, store it until the transcription is stopped. One resource ID can be used only for one transcription session.
Request example
Response example
-
Success
-
Failure
Start the service
Call start within five minutes after getting the resource ID to join the channel and start a transcription session.
After a successful request you get taskID in the HTTP response body. This ID is a unique identification of the current transcription session.
Request example
This is a simple request example to start the Real-Time STT service. Refer to Encrypt captions, Record captions, and Transcribe specified hosts for more feature configurations.
Response example
-
Success
-
Failure
Query service status
You can call query to find out the status of the transcription session multiple times during a transcription session. After a successful request, you get the status and related information in the response body.
Request example
Response example
-
Success
-
Failure
Update service
See Update service for details.
Stop the service
Call stop to stop transcribing. After a successful request, you get the status of the transcription session in the response body.
Request example
Considerations
API calls
- Call the
startmethod within 5 minutes after obtaining a resource ID. In case of timeout you'll need to request a new resource ID. - Since a transcription session is started and stopped with the same resource ID, once a session is started, it will automatically stop when the resource ID expires. The default validity time is 24 hours and up to 48 hours.
- String UIDs are supported only on a 128 host environment, with full support planned in the near future.
pubBotUidandsubBotUidareinttype UIDs that must be different to avoid unknown issues.
See also
Sample project
Agora provides a Postman collection with sample RESTful API requests for Real-Time STT.
Demo app and source code
Check our demo to try out Real-Time STT and evaluate its accuracy and latency.
You can also refer to the demo code on Github to see how captions and transcription are implemented. For more demo code, contact support@agora.io.
REST API middleware
Agora Go Backend Middleware is an open-source microservice that exposes a RESTful API designed to simplify Real-Time STT interactions with Agora. Written in Golang and powered by the Gin framework, this community project serves as a middleware to bridge front-end applications using Agora's Video SDK or Voice SDK with Agora's RESTful APIs.