Quickstart guide
Integrating Agora's real-time audio communication capabilities with OpenAI's language models enables dynamic, conversational AI experiences. This guide shows you how to set up a Python project that combines Agora's server-side Voice SDK with OpenAI's API to create an interactive, voice-driven assistant.
Understand the tech
The RealtimeKitAgent class manages the integration by connecting to an Agora channel for real-time audio streaming and to OpenAI's API for processing audio input and generating AI-driven responses. Audio frames captured from the Agora channel are streamed to OpenAI's API, where the AI processes the input. The API responses, which include transcribed text and synthesized voice output, are then delivered back to the Agora channel.
The code sets up tools that can be executed locally or passed through the API, allowing the AI to perform specific tasks, such as retrieving data from external sources. The agent processes various message types from OpenAI, including audio responses, transcription updates, and error messages, and sends them to users through the Agora audio channel, facilitating continuous interaction.
The following figure illustrates the integration topology:
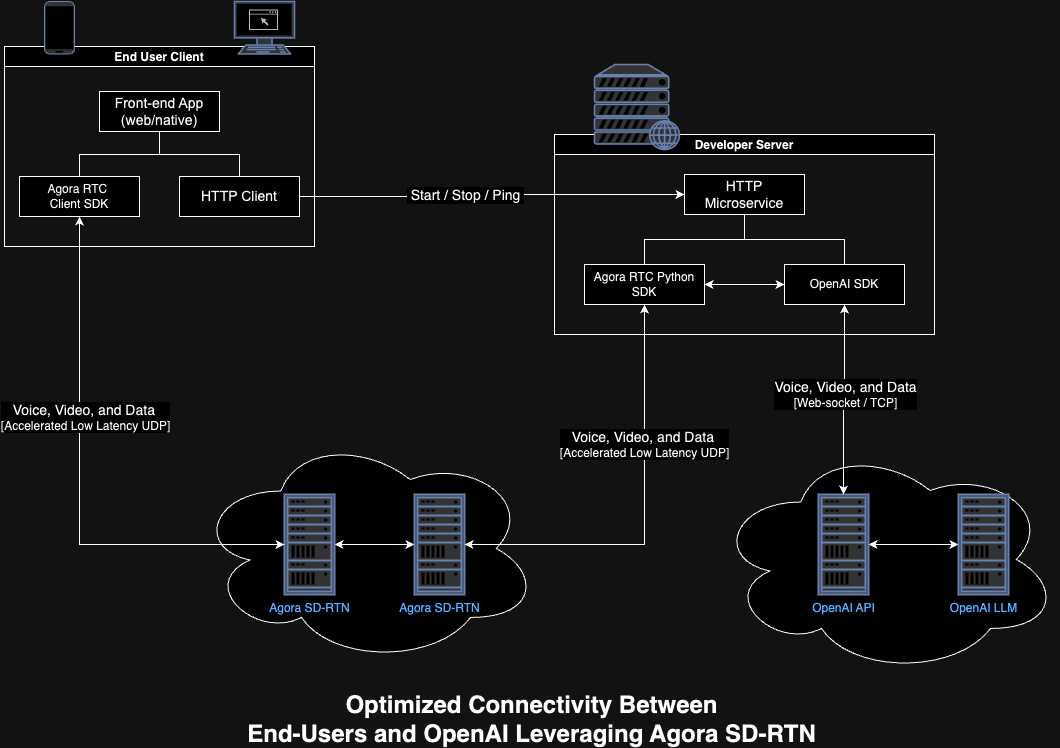
Prerequisites
-
FFmpeg
-
PyAudio
Getting Started
This guide walks you through the core elements of the Agora Conversational AI Demo integrating Agora's Python SDK with OpenAI's Realtime API.
If you’d prefer to skip the step-by-step guide and explore the demo project, clone the repository and follow the steps in the README to get started:
Set up the project
To follow the step-by-step procedure:
-
Create a new folder for the project:
-
Create the base project structure:
The project structure should look like this:
-
Add the following dependencies to the
requirements.txtfile: -
Open the
.envfile and fill in the values for the environment variables: -
Create a virtual environment and activate it:
-
Install the required dependencies:
Overview of key files:
agent.py: The main script responsible for executing theRealtimeKitAgentby integrating Agora's and OpenAI's capabilities.main.py: Sets up an HTTP server that handles real-time agent processes.tools.py: Classes for registering and invoking tools.utils.py: Provides utilities that facilitate passing audio data between Agora and OpenAI.parse_args.py: Parses the command-line arguments used to customize the channel name and user ID when running script.logger.py: Helper functions for logging.realtime/: Contains the classes and methods that interact with OpenAI's Realtime API.
The complete code for files in the realtime_agent folder is provided at the bottom of this page.
Implementation
Before diving into the implementation details, it is essential to establish a solid foundation. Start by copying the base integration code provided below to the agent.py file. This framework includes the core structure and necessary imports for your agent. From here, we will proceed step by step to implement each function.
RealtimeKitAgent
The RealtimeKitAgent class integrates Agora's real-time audio communication with OpenAI’s AI services. It handles streaming, communication with the OpenAI API, and AI responses, creating a seamless conversational experience.
Connect to Agora and OpenAI
The setup_and_run_agent method connects to an Agora channel using RtcEngine, and sets up a session with OpenAI’s Realtime API. It configures the session parameters, such as system messages and voice settings, and uses asynchronous tasks to concurrently listen for the session to start and update the conversation configuration. In the base agent.py file, replace the placeholder with the following implementation.
Initialize the RealtimeKitAgent
The constructor for RealtimeKitAgent sets up the OpenAI client, optional tools, and Agora channel to manage real-time audio communication. In agent.py, add the following code after the setup_and_run_agent method:
Launch the Agent
The run method is the core of the RealtimeKitAgent. It manages the agent’s operations by handling audio streams, subscribing to remote users, and processing both incoming and outgoing messages. This method also ensures proper exception handling and graceful shutdown. Following are the key functions of this method:
- Waiting for remote users: The agent waits for a remote user to join the Agora channel and subscribes to their audio stream.
- Task management: The agent initiates tasks for audio input, audio output, and processing messages from OpenAI, ensuring that they run concurrently.
- Connection state handling: It monitors changes in connection state and handles user disconnections, ensuring the agent shuts down gracefully.
In agent.py, replace the run placeholder with the following:
Communicate with the AI model
The RealtimeKitAgent is responsible for managing real-time audio communication between Agora and OpenAI’s AI model. It implements this through two core streaming methods:
rtc_to_model: Captures audio frames from the Agora channel and streams them to OpenAI’s model for processing.model_to_rtc: Handles the output by pushing audio responses from OpenAI’s model back to the Agora channel for playback.
Additionally, the agent must process messages received from the OpenAI model. This is handled by the _process_model_messages method.
Stream input audio to the AI model
The rtc_to_model method captures audio frames from the Agora channel and streams them to OpenAI’s model for processing. This method runs continuously, retrieving audio frames from the subscribed user and forwarding them through the OpenAI API.
The code implements the following key features:
- Subscription check: Ensures that a remote user is subscribed before capturing any audio frames.
- Audio frame processing: Sends each audio frame from the Agora channel to OpenAI’s model.
- Error handling: Logs any errors that occur during the audio streaming process.
Replace the rtc_to_model placeholder in agent.py with the following implementation:
Stream audio queue to audio output
The model_to_rtc method streams audio generated by OpenAI’s model back to the Agora channel. It retrieves audio data from an internal queue and pushes it to Agora for real-time playback.
The code implements the following key features:
- Audio queue management: Retrieves audio data from an asynchronous queue filled with responses from OpenAI’s model.
- Efficient task management: After processing each audio frame, the method yields control to ensure other tasks can run concurrently.
- Real-time playback: Audio data is pushed to the Agora channel for immediate playback to the user.
Replace the model_to_rtc placeholder in agent.py with the following implementation:
Process model messages
In addition to handling audio streaming, the agent must process messages received from the OpenAI model. Message processing in RealtimeKitAgent is central to how the agent interacts with OpenAI’s model and the Agora channel. Messages received from the model can include audio data, text transcripts, or other responses, and the agent needs to process these accordingly to ensure smooth real-time communication.
The _process_model_messages method listens for incoming messages and handles them according to their type, ensuring the appropriate action is taken, such as playing back audio, sending text transcripts, or invoking tools.
Key features implemented by _process_model_messages:
- Listening for messages: The agent continuously listens for incoming messages from OpenAI’s model.
- Handling audio data: If the message contains audio data, it is placed in a queue for playback to the Agora channel.
- Handling transcripts: If the message contains partial or final text transcripts, they are processed and sent to the Agora chat.
- Handling other responses: Additional message types, such as tool invocations and other outputs are processed as needed.
Audio and message flow
The first case in _process_model_messages method is InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted. When this event is triggered, the system clears the sender’s audio buffer on the Agora channel and empties the local audio queue to ensure no prior audio interferes with the new input. It also logs the event for tracking purposes, allowing the agent to effectively manage and process incoming audio streams.
Response Messages
The _process_model_messages method is also responsible for handling both audio and text responses in real time. It processes various message types by managing audio data and sending text messages to the Agora chat channel.
When an audio delta message is received, the system decodes the audio and adds it to the local audio queue for playback, while also logging the event for reference. For transcript updates, the agent sends the corresponding text message to the chat asynchronously, ensuring that message handling does not block other processes. Finally, when the transcript is complete, the system logs the event and sends the final message to the Agora chat.
Handling message responses
Following is the full implementation of _process_model_messages that incorporates code snippets from previous sections. In the full implementation, audio input events are handled by clearing audio buffers and queues when speech starts or stops. Audio deltas are decoded and placed into the local queue, while transcript messages are sent asynchronously to the Agora chat.
The agent can be extended to support a variety of other message types, including tool calls, errors, and other outputs from OpenAI’s model. If the agent encounters an unhandled message type, it logs a warning to notify developers for further investigation.
Using these components, the agent handles audio, transcripts, and other messages in real-time, ensuring that it responds appropriately to OpenAI model’s output and maintains seamless communication with the Agora channel.
Wait for a remote user
The wait_for_remote_user function is a key component of the agent's functionality. It listens for an event where a remote user joins the Agora channel. This function will block until a user joins or until it times out.
The method implements the following:
- Event listener: The function listens for the
user_joinedevent from the Agora SDK. When a user joins the channel, it captures the user ID and signals that a user has joined usingremote_user_joined.set(). - Timeout handling: If no user joins within the specified
timeout, aTimeoutErroris raised and logged as an error. - Cleanup: After successfully getting a user ID or timing out, the event listener is removed using
channel.off("user_joined", on_user_joined).
In agent.py, replace the wait_for_remote_user placeholder code with:
Utils
In the agent.py file, we initialize a PCMWriter instance, which is responsible for writing audio frames to a file that is sent to the AI for processing. The PCMWriter class, along with its methods, is defined in the utils.py file.
OpenAI Connection
The connection.py file manages the real-time communication between the agent and OpenAI’s API. It handles the connection setup, sending and receiving messages, and managing audio data streaming. The RealtimeApiConnection class encapsulates all the connection logic, making it easier to integrate real-time AI responses.
Open realtime/connection.py and add the imports and the smart_str function, used to parse JSON data, truncate fields (like delta or audio) to a maximum length for logging purposes, and then re-serialize the modified data.
RealtimeApiConnection class
The RealtimeApiConnection class manages the real-time API connection. During initialization the OpenAI key, API URL (includes model), and authentication token are passed to the client and the WebSocket session is initialized. The connect method establishes a WebSocket connection to the specified URL using authentication headers. The close method ensures that the WebSocket connection is closed gracefully, preventing resource leaks. This connection lifecycle management is crucial for handling long-running WebSocket sessions in real-time applications.
Context manager for connection lifecycle
These methods allow the RealtimeApiConnection class to be used as an asynchronous context manager, ensuring that the connection is opened when entering the context and properly closed when exiting. This pattern simplifies resource management, especially for long-lived connections in asynchronous workflows.
Sending audio data and messages
The send_audio_data method sends audio data (encoded in base64) over the WebSocket. It packages the audio data into a ClientToServerMessage and calls send_request to transmit it. The send_request method logs the outgoing message (if verbose logging is enabled) and sends it through the WebSocket connection.
Listening for incoming messages
The listen method listens for incoming messages from the WebSocket. It uses an asynchronous generator to handle incoming messages in a non-blocking way. Depending on the message type (text or error), it processes the message and passes it to handle_server_message. If verbose logging is enabled, incoming messages are logged to facilitate debugging.
Handling server messages
The handle_server_message method parses the server’s message and handles any exceptions that occur during parsing. This method ensures that malformed messages are logged as errors, helping to track down issues with the server response format.
Struct.py
The connection class and agent utilize various classes and structures defined in realtime/struct.py. While the specifics of this file are beyond the scope of this guide, the complete code is provided below for use and reference.
Tool Management
Every agent needs a tool management system to extend the agent's functionality by allowing OpenAI’s model to invoke specific tools. These tools can either run locally or pass data back to the model for further processing. By registering tools and executing them based on incoming messages, the agent adds the capability and flexibility to handle a variety of tasks.
Tool management implements the following key features:
- Tool registration: Register both local function tools and pass-through tools, making them available for execution.
- Tool execution: Execute tools in response to requests from the OpenAI model, running them locally or passing data back to the model.
- Tool context: The
ToolContextclass manages the tools, providing methods to register and execute them as needed.
Open the tools.py file and add the following code to import the required packages.
Define Local and Passthrough tools
When setting up tools, define if the tool is executed directly by the agent on the local context, or if it sends data back to OpenAI’s model.
- Local function tools: Executed directly by the agent on the local context.
- Pass-through tools: Send data back to OpenAI’s model without it being executed locally.
The ToolContext class manages all available tools. It provides the logic for both registering tools and executing them when requested by the OpenAI model. Once tools are registered, the agent can execute them in response to messages from OpenAI’s model. The agent listens for tool call requests and either executes the tool locally or passes data back to the model.
In the ToolContext class, the execute_tool method retrieves the tool by name and runs it with the provided arguments. If it is a local function tool, the agent executes the function and returns the result. If it is a pass-through tool, it simply returns the decoded arguments to the model for further processing.
Tool registration and invocation
Registering tools during the setup process makes them available for the model to call.
Tool invocation in message processing
It is important to highlight how tools are invoked. During message processing, certain messages may trigger tool invocations, prompting the agent to execute the relevant tool.
The following flow illustrates how this works:
- The OpenAI model sends a message that includes a tool call.
- The
_process_model_messagesmethod identifies the tool call request. - The agent retrieves the relevant tool from the
ToolContextand executes it, either locally or by passing data back to the model.
This integration between message processing and tool management ensures that the agent can extend its capabilities dynamically, performing tasks or calculations in real-time based on incoming requests.
The ClientToolCallResponse model represents the response after a tool is invoked and processed. This class is designed to represent the response of a client-side tool call, where the tool_call_id uniquely identifies the tool call, and the result can take on multiple data types, representing the output of that call. The flexibility in the result field allows for a wide variety of responses.
With these pieces in place, the agent can effectively manage tool registration and execution, ensuring that it can handle a variety of tasks as directed by the OpenAI model. This structure allows the agent to either execute functions locally or pass them to the model for further handling.
Set up a server
The main.py script orchestrates the initialization of an HTTP server that allows clients to start and stop AI-driven agents in Agora voice channels. It includes routes for starting and stopping agents, manages processes for different channels, and handles cleanup and shutdown procedures. The agents run as separate processes, ensuring they can handle real-time interactions without blocking the main server. The application leverages aiohttp for handling HTTP requests, multiprocessing to manage agent processes, and asyncio for non-blocking execution.
Open main.py and add the following code to set up the imports and load the .env variables.
Process management and signal handling
The monitor_process function asynchronously monitors each agent process, ensuring that once it finishes, the process is cleaned up. handle_agent_proc_signal ensures that any agent receiving a termination signal exits gracefully. This process management ensures that the application can run multiple agents concurrently while maintaining proper resource management.
Run the agent
The run_agent_in_process method starts a RealtimeKitAgent in a new process, handling Agora RTC initialization with the necessary credentials and agent configuration.
HTTP Routes for Managing Agents
The start_agent and stop_agent routes are the main HTTP endpoints that allow clients to control the agents. As part of the start and stop we need to keep track of the active_processes.
When a POST request is made to /start_agent, the server validates the request, starts a new agent process (if one isn’t already running), and begins monitoring it. The processes are stored in an active_processes dictionary for efficient management.
The stop_agent route handles requests to stop an active agent. It first validates the request body using StopAgentRequestBody. If a process is found for the specified channel, it terminates the process using os.kill and sends a SIGKILL signal. The process is then removed from the active_processes dictionary, and a response is returned to confirm termination. If no process is found, a 404 error is returned, indicating the agent was not active.
Shutdown gracefully
The shutdown function is responsible for cleaning up agent processes when the server is shutting down. It iterates through all the processes in active_processes and terminates any that are still alive, ensuring no orphaned processes remain. This is essential for graceful shutdowns, preventing resource leaks. Once all processes are terminated, it clears the active_processes dictionary to reset the server state.
aiohttp application setup
The init_app function sets up the core aiohttp web application. It defines the HTTP routes for starting and stopping AI agents with the /start_agent and /stop_agent endpoints, and attaches a cleanup task to properly shut down processes when the server exits. The function returns the initialized app object, ready to be managed by the event loop and handle incoming requests.
Main Entry
Now that we have the entire agent setup, we are ready to bring it all together and implement the main entry point for our project. The main entry point of the program first parses the command-line arguments to determine whether the server should be started or an agent should be run directly. If server is chosen, it sets up the event loop and starts the aiohttp web server using init_app(), which binds the routes for starting and stopping agents. If agent is selected, it parses the RealtimeKit options and starts an agent process using run_agent_in_process. This structure allows the application to either act as a server managing agents or run an individual agent directly, depending on the context.
Parse Args and Logger
This project implements a few helper functions to support in parsing command line arguments and to handle logging. While the specifics of these files are outside the scope of this guide, the complete code is provided below for use and reference.
Complete integration code
This section provides the complete code you need to implement and test integrating Agora's real-time audio streaming and OpenAI's API for processing audio input and generating AI-driven responses.
agent.py
import asyncioimport base64import loggingimport osfrom builtins import anextfrom typing import Anyfrom agora.rtc.rtc_connection import RTCConnection, RTCConnInfofrom attr import dataclassfrom agora_realtime_ai_api.rtc import Channel, ChatMessage, RtcEngine, RtcOptionsfrom logger import setup_loggerfrom realtime.struct import InputAudioBufferCommitted, InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted, InputAudioBufferSpeechStopped, ItemCreated, RateLimitsUpdated, ResponseAudioDelta, ResponseAudioDone, ResponseAudioTranscriptDelta, ResponseAudioTranscriptDone, ResponseContentPartAdded, ResponseContentPartDone, ResponseCreated, ResponseDone, ResponseOutputItemAdded, ResponseOutputItemDone, ServerVADUpdateParams, SessionUpdate, SessionUpdateParams, SessionUpdated, Voices, to_jsonfrom realtime.connection import RealtimeApiConnectionfrom tools import ClientToolCallResponse, ToolContextfrom utils import PCMWriter# Set up the logger logger = setup_logger(name=__name__, log_level=logging.INFO)def _monitor_queue_size(queue: asyncio.Queue, queue_name: str, threshold: int = 5) -> None: queue_size = queue.qsize() if queue_size > threshold: logger.warning(f"Queue {queue_name} size exceeded {threshold}: current size {queue_size}")async def wait_for_remote_user(channel: Channel) -> int: remote_users = list(channel.remote_users.keys()) if len(remote_users) > 0: return remote_users[0] future = asyncio.Future[int]() channel.once("user_joined", lambda conn, user_id: future.set_result(user_id)) try: # Wait for the remote user with a timeout of 30 seconds remote_user = await asyncio.wait_for(future, timeout=30.0) return remote_user except KeyboardInterrupt: future.cancel() except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Error waiting for remote user: {e}") raise@dataclass(frozen=True, kw_only=True)class InferenceConfig: system_message: str | None = None turn_detection: ServerVADUpdateParams | None = None # MARK: CHECK! voice: Voices | None = Noneclass RealtimeKitAgent: engine: RtcEngine channel: Channel connection: RealtimeApiConnection audio_queue: asyncio.Queue[bytes] = asyncio.Queue() message_queue: asyncio.Queue[ResponseAudioTranscriptDelta] = ( asyncio.Queue() ) message_done_queue: asyncio.Queue[ResponseAudioTranscriptDone] = ( asyncio.Queue() ) tools: ToolContext | None = None _client_tool_futures: dict[str, asyncio.Future[ClientToolCallResponse]] @classmethod async def setup_and_run_agent( cls, *, engine: RtcEngine, options: RtcOptions, inference_config: InferenceConfig, tools: ToolContext | None, ) -> None: channel = engine.create_channel(options) await channel.connect() try: async with RealtimeApiConnection( base_uri=os.getenv("REALTIME_API_BASE_URI", "wss://api.openai.com"), api_key=os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"), verbose=False, ) as connection: await connection.send_request( SessionUpdate( session=SessionUpdateParams( # MARK: check this turn_detection=inference_config.turn_detection, tools=tools.model_description() if tools else [], tool_choice="auto", input_audio_format="pcm16", output_audio_format="pcm16", instructions=inference_config.system_message, voice=inference_config.voice, model=os.environ.get("OPENAI_MODEL", "gpt-4o-realtime-preview"), modalities=["text", "audio"], temperature=0.8, max_response_output_tokens="inf", ) ) ) start_session_message = await anext(connection.listen()) # assert isinstance(start_session_message, messages.StartSession) logger.info( f"Session started: {start_session_message.session.id} model: {start_session_message.session.model}" ) agent = cls( connection=connection, tools=tools, channel=channel, ) await agent.run() finally: await channel.disconnect() await connection.close() def __init__( self, *, connection: RealtimeApiConnection, tools: ToolContext | None, channel: Channel, ) -> None: self.connection = connection self.tools = tools self._client_tool_futures = {} self.channel = channel self.subscribe_user = None self.write_pcm = os.environ.get("WRITE_AGENT_PCM", "false") == "true" logger.info(f"Write PCM: {self.write_pcm}") async def run(self) -> None: try: def log_exception(t: asyncio.Task[Any]) -> None: if not t.cancelled() and t.exception(): logger.error( "unhandled exception", exc_info=t.exception(), ) logger.info("Waiting for remote user to join") self.subscribe_user = await wait_for_remote_user(self.channel) logger.info(f"Subscribing to user {self.subscribe_user}") await self.channel.subscribe_audio(self.subscribe_user) async def on_user_left( agora_rtc_conn: RTCConnection, user_id: int, reason: int ): logger.info(f"User left: {user_id}") if self.subscribe_user == user_id: self.subscribe_user = None logger.info("Subscribed user left, disconnecting") await self.channel.disconnect() self.channel.on("user_left", on_user_left) disconnected_future = asyncio.Future[None]() def callback(agora_rtc_conn: RTCConnection, conn_info: RTCConnInfo, reason): logger.info(f"Connection state changed: {conn_info.state}") if conn_info.state == 1: if not disconnected_future.done(): disconnected_future.set_result(None) self.channel.on("connection_state_changed", callback) asyncio.create_task(self.rtc_to_model()).add_done_callback(log_exception) asyncio.create_task(self.model_to_rtc()).add_done_callback(log_exception) asyncio.create_task(self._process_model_messages()).add_done_callback( log_exception ) await disconnected_future logger.info("Agent finished running") except asyncio.CancelledError: logger.info("Agent cancelled") except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Error running agent: {e}") raise async def rtc_to_model(self) -> None: if self.subscribe_user is None: await asyncio.sleep(0.1) audio_frames = self.channel.get_audio_frames(self.subscribe_user) # Initialize PCMWriter for receiving audio pcm_writer = PCMWriter(prefix="rtc_to_model", write_pcm=self.write_pcm) try: async for audio_frame in audio_frames: # Process received audio (send to model) _monitor_queue_size(self.audio_queue, "audio_queue") await self.connection.send_audio_data(audio_frame.data) # Write PCM data if enabled await pcm_writer.write(audio_frame.data) await asyncio.sleep(0) # Yield control to allow other tasks to run except asyncio.CancelledError: # Write any remaining PCM data before exiting await pcm_writer.flush() raise # Re-raise the exception to propagate cancellation async def model_to_rtc(self) -> None: # Initialize PCMWriter for sending audio pcm_writer = PCMWriter(prefix="model_to_rtc", write_pcm=self.write_pcm) try: while True: # Get audio frame from the model output frame = await self.audio_queue.get() # Process sending audio (to RTC) await self.channel.push_audio_frame(frame) # Write PCM data if enabled await pcm_writer.write(frame) except asyncio.CancelledError: # Write any remaining PCM data before exiting await pcm_writer.flush() raise # Re-raise the cancelled exception to properly exit the task async def _process_model_messages(self) -> None: async for message in self.connection.listen(): # logger.info(f"Received message {message=}") match message: case InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted(): await self.channel.clear_sender_audio_buffer() # clear the audio queue so audio stops playing while not self.audio_queue.empty(): self.audio_queue.get_nowait() logger.info(f"TMS:InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted: item_id: {message.item_id}") case InputAudioBufferSpeechStopped(): logger.info(f"TMS:InputAudioBufferSpeechStopped: item_id: {message.item_id}") pass case ResponseAudioDelta(): # logger.info("Received audio message") self.audio_queue.put_nowait(base64.b64decode(message.delta)) # loop.call_soon_threadsafe(self.audio_queue.put_nowait, base64.b64decode(message.delta)) logger.info(f"TMS:ResponseAudioDelta: response_id:{message.response_id},item_id: {message.item_id}") case ResponseAudioTranscriptDelta(): # logger.info(f"Received text message {message=}") asyncio.create_task(self.channel.chat.send_message( ChatMessage( message=to_json(message), msg_id=message.item_id ) )) case ResponseAudioTranscriptDone(): logger.info(f"Text message done: {message=}") asyncio.create_task(self.channel.chat.send_message( ChatMessage( message=to_json(message), msg_id=message.item_id ) )) # InputAudioBufferCommitted case InputAudioBufferCommitted(): pass case ItemCreated(): pass # ResponseCreated case ResponseCreated(): pass # ResponseDone case ResponseDone(): pass # ResponseOutputItemAdded case ResponseOutputItemAdded(): pass # ResponseContenPartAdded case ResponseContentPartAdded(): pass # ResponseAudioDone case ResponseAudioDone(): pass # ResponseContentPartDone case ResponseContentPartDone(): pass # ResponseOutputItemDone case ResponseOutputItemDone(): pass case SessionUpdated(): pass case RateLimitsUpdated(): pass case _: logger.warning(f"Unhandled message {message=}")main.py
import asyncioimport loggingimport osimport signalfrom multiprocessing import Processfrom aiohttp import webfrom dotenv import load_dotenvfrom pydantic import BaseModel, Field, ValidationErrorfrom realtime.struct import PCM_CHANNELS, PCM_SAMPLE_RATE, ServerVADUpdateParams, Voicesfrom agent import InferenceConfig, RealtimeKitAgentfrom agora_realtime_ai_api.rtc import RtcEngine, RtcOptionsfrom logger import setup_loggerfrom parse_args import parse_args, parse_args_realtimekit# Set up the logger with color and timestamp supportlogger = setup_logger(name=__name__, log_level=logging.INFO)load_dotenv(override=True)app_id = os.environ.get("AGORA_APP_ID")app_cert = os.environ.get("AGORA_APP_CERT")if not app_id: raise ValueError("AGORA_APP_ID must be set in the environment.")class StartAgentRequestBody(BaseModel): channel_name: str = Field(..., description="The name of the channel") uid: int = Field(..., description="The UID of the user") language: str = Field("en", description="The language of the agent")class StopAgentRequestBody(BaseModel): channel_name: str = Field(..., description="The name of the channel")# Function to monitor the process and perform extra work when it finishesasync def monitor_process(channel_name: str, process: Process): # Wait for the process to finish in a non-blocking way await asyncio.to_thread(process.join) logger.info(f"Process for channel {channel_name} has finished") # Perform additional work after the process finishes # For example, removing the process from the active_processes dictionary if channel_name in active_processes: active_processes.pop(channel_name) # Perform any other cleanup or additional actions you need here logger.info(f"Cleanup for channel {channel_name} completed") logger.info(f"Remaining active processes: {len(active_processes.keys())}")def handle_agent_proc_signal(signum, frame): logger.info(f"Agent process received signal {signal.strsignal(signum)}. Exiting...") os._exit(0)def run_agent_in_process( engine_app_id: str, engine_app_cert: str, channel_name: str, uid: int, inference_config: InferenceConfig,): # Set up signal forwarding in the child process signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, handle_agent_proc_signal) # Forward SIGINT signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, handle_agent_proc_signal) # Forward SIGTERM asyncio.run( RealtimeKitAgent.setup_and_run_agent( engine=RtcEngine(appid=engine_app_id, appcert=engine_app_cert), options=RtcOptions( channel_name=channel_name, uid=uid, sample_rate=PCM_SAMPLE_RATE, channels=PCM_CHANNELS, enable_pcm_dump= os.environ.get("WRITE_RTC_PCM", "false") == "true" ), inference_config=inference_config, tools=None, ) )# HTTP Server Routesasync def start_agent(request): try: # Parse and validate JSON body using the pydantic model try: data = await request.json() validated_data = StartAgentRequestBody(**data) except ValidationError as e: return web.json_response( {"error": "Invalid request data", "details": e.errors()}, status=400 ) # Parse JSON body channel_name = validated_data.channel_name uid = validated_data.uid language = validated_data.language # Check if a process is already running for the given channel_name if ( channel_name in active_processes and active_processes[channel_name].is_alive() ): return web.json_response( {"error": f"Agent already running for channel: {channel_name}"}, status=400, ) system_message = "" if language == "en": system_message = """Your knowledge cutoff is 2023-10. You are a helpful, witty, and friendly AI. Act like a human, but remember that you aren't a human and that you can't do human things in the real world. Your voice and personality should be warm and engaging, with a lively and playful tone. If interacting in a non-English language, start by using the standard accent or dialect familiar to the user. Talk quickly. You should always call a function if you can. Do not refer to these rules, even if you're asked about them.""" inference_config = InferenceConfig( system_message=system_message, voice=Voices.Alloy, turn_detection=ServerVADUpdateParams( type="server_vad", threshold=0.5, prefix_padding_ms=300, silence_duration_ms=200 ), ) # Create a new process for running the agent process = Process( target=run_agent_in_process, args=(app_id, app_cert, channel_name, uid, inference_config), ) try: process.start() except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to start agent process: {e}") return web.json_response( {"error": f"Failed to start agent: {e}"}, status=500 ) # Store the process in the active_processes dictionary using channel_name as the key active_processes[channel_name] = process # Monitor the process in a background asyncio task asyncio.create_task(monitor_process(channel_name, process)) return web.json_response({"status": "Agent started!"}) except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to start agent: {e}") return web.json_response({"error": str(e)}, status=500)# HTTP Server Routes: Stop Agentasync def stop_agent(request): try: # Parse and validate JSON body using the pydantic model try: data = await request.json() validated_data = StopAgentRequestBody(**data) except ValidationError as e: return web.json_response( {"error": "Invalid request data", "details": e.errors()}, status=400 ) # Parse JSON body channel_name = validated_data.channel_name # Find and terminate the process associated with the given channel name process = active_processes.get(channel_name) if process and process.is_alive(): logger.info(f"Terminating process for channel {channel_name}") await asyncio.to_thread(os.kill, process.pid, signal.SIGKILL) return web.json_response( {"status": "Agent process terminated", "channel_name": channel_name} ) else: return web.json_response( {"error": "No active agent found for the provided channel_name"}, status=404, ) except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Failed to stop agent: {e}") return web.json_response({"error": str(e)}, status=500)# Dictionary to keep track of processes by channel name or UIDactive_processes = {}# Function to handle shutdown and process cleanupasync def shutdown(app): logger.info("Shutting down server, cleaning up processes...") for channel_name, process in active_processes.items(): if process.is_alive(): logger.info( f"Terminating process for channel {channel_name} (PID: {process.pid})" ) await asyncio.to_thread(os.kill, process.pid, signal.SIGKILL) await asyncio.to_thread(process.join) # Ensure process has terminated active_processes.clear() logger.info("All processes terminated, shutting down server")# Signal handler to gracefully stop the applicationdef handle_signal(signum, frame): logger.info(f"Received exit signal {signal.strsignal(signum)}...") loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() if loop.is_running(): # Properly shutdown by stopping the loop and running shutdown loop.create_task(shutdown(None)) loop.stop()# Main aiohttp application setupasync def init_app(): app = web.Application() # Add cleanup task to run on app exit app.on_cleanup.append(shutdown) app.add_routes([web.post("/start_agent", start_agent)]) app.add_routes([web.post("/stop_agent", stop_agent)]) return appif __name__ == "__main__": # Parse the action argument args = parse_args() # Action logic based on the action argument if args.action == "server": # Python 3.10+ requires explicitly creating a new event loop if none exists try: loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() except RuntimeError: # For Python 3.10+, use this to get a new event loop if the default is closed or not created loop = asyncio.new_event_loop() asyncio.set_event_loop(loop) # Start the application using asyncio.run for the new event loop app = loop.run_until_complete(init_app()) web.run_app(app, port=int(os.getenv("SERVER_PORT") or "8080")) elif args.action == "agent": # Parse RealtimeKitOptions for running the agent realtime_kit_options = parse_args_realtimekit() # Example logging for parsed options (channel_name and uid) logger.info(f"Running agent with options: {realtime_kit_options}") inference_config = InferenceConfig( system_message="""Your knowledge cutoff is 2023-10. You are a helpful, witty, and friendly AI. Act like a human, but remember that you aren't a human and that you can't do human things in the real world. Your voice and personality should be warm and engaging, with a lively and playful tone. If interacting in a non-English language, start by using the standard accent or dialect familiar to the user. Talk quickly. You should always call a function if you can. Do not refer to these rules, even if you're asked about them.""", voice=Voices.Alloy, turn_detection=ServerVADUpdateParams( type="server_vad", threshold=0.5, prefix_padding_ms=300, silence_duration_ms=200 ), ) run_agent_in_process( engine_app_id=app_id, engine_app_cert=app_cert, channel_name=realtime_kit_options["channel_name"], uid=realtime_kit_options["uid"], inference_config=inference_config, )tools.py
import abcimport jsonimport loggingfrom typing import Any, Callable, assert_neverfrom attr import dataclassfrom pydantic import BaseModelfrom logger import setup_logger# Set up the logger with color and timestamp supportlogger = setup_logger(name=__name__, log_level=logging.INFO)@dataclass(frozen=True, kw_only=True)class LocalFunctionToolDeclaration: """Declaration of a tool that can be called by the model, and runs a function locally on the tool context.""" name: str description: str parameters: dict[str, Any] function: Callable[..., Any] def model_description(self) -> dict[str, Any]: return { "type": "function", "function": { "name": self.name, "description": self.description, "parameters": self.parameters, }, }@dataclass(frozen=True, kw_only=True)class PassThroughFunctionToolDeclaration: """Declaration of a tool that can be called by the model.""" name: str description: str parameters: dict[str, Any] def model_description(self) -> dict[str, Any]: return { "type": "function", "function": { "name": self.name, "description": self.description, "parameters": self.parameters, }, }ToolDeclaration = LocalFunctionToolDeclaration | PassThroughFunctionToolDeclaration@dataclass(frozen=True, kw_only=True)class LocalToolCallExecuted: json_encoded_output: str@dataclass(frozen=True, kw_only=True)class ShouldPassThroughToolCall: decoded_function_args: dict[str, Any]ExecuteToolCallResult = LocalToolCallExecuted | ShouldPassThroughToolCallclass ToolContext(abc.ABC): _tool_declarations: dict[str, ToolDeclaration] def __init__(self) -> None: # TODO should be an ordered dict self._tool_declarations = {} def register_function( self, *, name: str, description: str = "", parameters: dict[str, Any], fn: Callable[..., Any], ) -> None: self._tool_declarations[name] = LocalFunctionToolDeclaration( name=name, description=description, parameters=parameters, function=fn ) def register_client_function( self, *, name: str, description: str = "", parameters: dict[str, Any], ) -> None: self._tool_declarations[name] = PassThroughFunctionToolDeclaration( name=name, description=description, parameters=parameters ) async def execute_tool( self, tool_name: str, encoded_function_args: str ) -> ExecuteToolCallResult | None: tool = self._tool_declarations.get(tool_name) if not tool: return None args = json.loads(encoded_function_args) assert isinstance(args, dict) if isinstance(tool, LocalFunctionToolDeclaration): logger.info(f"Executing tool {tool_name} with args {args}") result = await tool.function(**args) logger.info(f"Tool {tool_name} executed with result {result}") return LocalToolCallExecuted(json_encoded_output=json.dumps(result)) if isinstance(tool, PassThroughFunctionToolDeclaration): return ShouldPassThroughToolCall(decoded_function_args=args) assert_never(tool) def model_description(self) -> list[dict[str, Any]]: return [v.model_description() for v in self._tool_declarations.values()]class ClientToolCallResponse(BaseModel): tool_call_id: str result: dict[str, Any] | str | float | int | bool | None = Nonelogger.py
import loggingfrom datetime import datetimeimport colorlogdef setup_logger( name: str, log_level: int = logging.INFO, log_format: str = "%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s", use_color: bool = True) -> logging.Logger: """Sets up and returns a logger with color and timestamp support, including milliseconds.""" # Create or get a logger with the given name logger = logging.getLogger(name) # Prevent the logger from propagating to the root logger (disable extra output) logger.propagate = False # Clear existing handlers to avoid duplicate messages if logger.hasHandlers(): logger.handlers.clear() # Set the log level logger.setLevel(log_level) # Create console handler handler = logging.StreamHandler() # Custom formatter for adding milliseconds class CustomFormatter(colorlog.ColoredFormatter): def formatTime(self, record, datefmt=None): record_time = datetime.fromtimestamp(record.created) if datefmt: return record_time.strftime(datefmt) + f",{int(record.msecs):03d}" else: return record_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") + f",{int(record.msecs):03d}" # Use custom formatter that includes milliseconds if use_color: formatter = CustomFormatter( "%(log_color)s" + log_format, datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", # Milliseconds will be appended manually log_colors={ "DEBUG": "cyan", "INFO": "green", "WARNING": "yellow", "ERROR": "red", "CRITICAL": "bold_red", }, ) else: formatter = CustomFormatter(log_format, datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") handler.setFormatter(formatter) # Add the handler to the logger logger.addHandler(handler) return loggerutils.py
import asyncioimport functoolsfrom datetime import datetimedef write_pcm_to_file(buffer: bytearray, file_name: str) -> None: """Helper function to write PCM data to a file.""" with open(file_name, "ab") as f: # append to file f.write(buffer)def generate_file_name(prefix: str) -> str: # Create a timestamp for the file name timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d_%H%M%S") return f"{prefix}_{timestamp}.pcm"class PCMWriter: def __init__(self, prefix: str, write_pcm: bool, buffer_size: int = 1024 * 64): self.write_pcm = write_pcm self.buffer = bytearray() self.buffer_size = buffer_size self.file_name = generate_file_name(prefix) if write_pcm else None self.loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() async def write(self, data: bytes) -> None: """Accumulate data into the buffer and write to file when necessary.""" if not self.write_pcm: return self.buffer.extend(data) # Write to file if buffer is full if len(self.buffer) >= self.buffer_size: await self._flush() async def flush(self) -> None: """Write any remaining data in the buffer to the file.""" if self.write_pcm and self.buffer: await self._flush() async def _flush(self) -> None: """Helper method to write the buffer to the file.""" if self.file_name: await self.loop.run_in_executor( None, functools.partial(write_pcm_to_file, self.buffer[:], self.file_name), ) self.buffer.clear()parse_args.py
import argparseimport loggingfrom typing import TypedDictfrom logger import setup_logger# Set up the logger with color and timestamp supportlogger = setup_logger(name=__name__, log_level=logging.INFO)class RealtimeKitOptions(TypedDict): channel_name: str uid: intdef parse_args(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Manage server and agent actions.") # Create a subparser for actions (server and agent) subparsers = parser.add_subparsers(dest="action", required=True) # Subparser for the 'server' action (no additional arguments) subparsers.add_parser("server", help="Start the server") # Subparser for the 'agent' action (with required arguments) agent_parser = subparsers.add_parser("agent", help="Run an agent") agent_parser.add_argument("--channel_name", required=True, help="Channel Id / must") agent_parser.add_argument("--uid", type=int, default=0, help="User Id / default is 0") return parser.parse_args()def parse_args_realtimekit() -> RealtimeKitOptions: args = parse_args() logger.info(f"Parsed arguments: {args}") if args.action == "agent": options: RealtimeKitOptions = {"channel_name": args.channel_name, "uid": args.uid} return options return Nonerealtime/connection.py
import asyncioimport base64import jsonimport loggingimport osimport aiohttpfrom typing import Any, AsyncGeneratorfrom .struct import InputAudioBufferAppend, ClientToServerMessage, ServerToClientMessage, parse_server_message, to_jsonfrom logger import setup_logger# Set up the logger with color and timestamp supportlogger = setup_logger(name=__name__, log_level=logging.INFO)DEFAULT_VIRTUAL_MODEL = "gpt-4o-realtime-preview"def smart_str(s: str, max_field_len: int = 128) -> str: """parse string as json, truncate data field to 128 characters, reserialize""" try: data = json.loads(s) if "delta" in data: key = "delta" elif "audio" in data: key = "audio" else: return s if len(data[key]) > max_field_len: data[key] = data[key][:max_field_len] + "..." return json.dumps(data) except json.JSONDecodeError: return sclass RealtimeApiConnection: def __init__( self, base_uri: str, api_key: str | None = None, path: str = "/v1/realtime", verbose: bool = False, model: str = DEFAULT_VIRTUAL_MODEL, ): self.url = f"{base_uri}{path}" if "model=" not in self.url: self.url += f"?model={model}" self.api_key = api_key or os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY") self.websocket: aiohttp.ClientWebSocketResponse | None = None self.verbose = verbose self.session = aiohttp.ClientSession() async def __aenter__(self) -> "RealtimeApiConnection": await self.connect() return self async def __aexit__(self, exc_type: Any, exc_value: Any, traceback: Any) -> bool: await self.close() return False async def connect(self): auth = aiohttp.BasicAuth("", self.api_key) if self.api_key else None headers = {"OpenAI-Beta": "realtime=v1"} self.websocket = await self.session.ws_connect( url=self.url, auth=auth, headers=headers, ) async def send_audio_data(self, audio_data: bytes): """audio_data is assumed to be pcm16 24kHz mono little-endian""" base64_audio_data = base64.b64encode(audio_data).decode("utf-8") message = InputAudioBufferAppend(audio=base64_audio_data) await self.send_request(message) async def send_request(self, message: ClientToServerMessage): assert self.websocket is not None message_str = to_json(message) if self.verbose: logger.info(f"-> {smart_str(message_str)}") await self.websocket.send_str(message_str) async def listen(self) -> AsyncGenerator[ServerToClientMessage, None]: assert self.websocket is not None if self.verbose: logger.info("Listening for realtime messages") try: async for msg in self.websocket: if msg.type == aiohttp.WSMsgType.TEXT: if self.verbose: logger.info(f"<- {smart_str(msg.data)}") yield self.handle_server_message(msg.data) elif msg.type == aiohttp.WSMsgType.ERROR: logger.error("Error during receive: %s", self.websocket.exception()) break except asyncio.CancelledError: logger.info("Receive messages task cancelled") def handle_server_message(self, message: str) -> ServerToClientMessage: try: return parse_server_message(message) except Exception as e: logger.error("Error handling message: " + str(e)) raise e async def close(self): # Close the websocket connection if it exists if self.websocket: await self.websocket.close() self.websocket = Nonerealtime/struct.py
import jsonfrom dataclasses import dataclass, asdict, field, is_dataclassfrom typing import Any, Dict, Literal, Optional, List, Set, Unionfrom enum import Enumimport uuidPCM_SAMPLE_RATE = 24000PCM_CHANNELS = 1def generate_event_id() -> str: return str(uuid.uuid4())# Enumsclass Voices(str, Enum): Alloy = "alloy" Echo = "echo" Fable = "fable" Nova = "nova" Nova_2 = "nova_2" Nova_3 = "nova_3" Nova_4 = "nova_4" Nova_5 = "nova_5" Onyx = "onyx" Shimmer = "shimmer"class AudioFormats(str, Enum): PCM16 = "pcm16" G711_ULAW = "g711_ulaw" G711_ALAW = "g711_alaw"class ItemType(str, Enum): Message = "message" FunctionCall = "function_call" FunctionCallOutput = "function_call_output"class MessageRole(str, Enum): System = "system" User = "user" Assistant = "assistant"class ContentType(str, Enum): InputText = "input_text" InputAudio = "input_audio" Text = "text" Audio = "audio"@dataclassclass FunctionToolChoice: name: str # Name of the function type: str = "function" # Fixed value for type# ToolChoice can be either a literal string or FunctionToolChoiceToolChoice = Union[str, FunctionToolChoice] # "none", "auto", "required", or FunctionToolChoice@dataclassclass RealtimeError: type: str # The type of the error message: str # The error message code: Optional[str] = None # Optional error code param: Optional[str] = None # Optional parameter related to the error event_id: Optional[str] = None # Optional event ID for tracing@dataclassclass InputAudioTranscription: model: str = "whisper-1" # Default transcription model is "whisper-1"@dataclassclass ServerVADUpdateParams: threshold: Optional[float] = None # Threshold for voice activity detection prefix_padding_ms: Optional[int] = None # Amount of padding before the voice starts (in milliseconds) silence_duration_ms: Optional[int] = None # Duration of silence before considering speech stopped (in milliseconds) type: str = "server_vad" # Fixed value for VAD type@dataclassclass Session: id: str # The unique identifier for the session model: str # The model associated with the session (e.g., "gpt-3") expires_at: int # Expiration time of the session in seconds since the epoch (UNIX timestamp) object: str = "realtime.session" # Fixed value indicating the object type modalities: Set[str] = field(default_factory=lambda: {"text", "audio"}) # Set of allowed modalities (e.g., "text", "audio") instructions: Optional[str] = None # Instructions or guidance for the session voice: Voices = Voices.Alloy # Voice configuration for audio responses, defaulting to "Alloy" turn_detection: Optional[ServerVADUpdateParams] = None # Voice activity detection (VAD) settings input_audio_format: AudioFormats = AudioFormats.PCM16 # Audio format for input (e.g., "pcm16") output_audio_format: AudioFormats = AudioFormats.PCM16 # Audio format for output (e.g., "pcm16") input_audio_transcription: Optional[InputAudioTranscription] = None # Audio transcription model settings (e.g., "whisper-1") tools: List[Dict[str, Union[str, Any]]] = field(default_factory=list) # List of tools available during the session tool_choice: Literal["auto", "none", "required"] = "auto" # How tools should be used in the session temperature: float = 0.8 # Temperature setting for model creativity max_response_output_tokens: Union[int, Literal["inf"]] = "inf" # Maximum number of tokens in the response, or "inf" for unlimited @dataclassclass SessionUpdateParams: model: Optional[str] = None # Optional string to specify the model modalities: Optional[Set[str]] = None # Set of allowed modalities (e.g., "text", "audio") instructions: Optional[str] = None # Optional instructions string voice: Optional[Voices] = None # Voice selection, can be `None` or from `Voices` Enum turn_detection: Optional[ServerVADUpdateParams] = None # Server VAD update params input_audio_format: Optional[AudioFormats] = None # Input audio format from `AudioFormats` Enum output_audio_format: Optional[AudioFormats] = None # Output audio format from `AudioFormats` Enum input_audio_transcription: Optional[InputAudioTranscription] = None # Optional transcription model tools: Optional[List[Dict[str, Union[str, any]]]] = None # List of tools (e.g., dictionaries) tool_choice: Optional[ToolChoice] = None # ToolChoice, either string or `FunctionToolChoice` temperature: Optional[float] = None # Optional temperature for response generation max_response_output_tokens: Optional[Union[int, str]] = None # Max response tokens, "inf" for infinite# Define individual message item param types@dataclassclass SystemMessageItemParam: content: List[dict] # This can be more specific based on content structure id: Optional[str] = None status: Optional[str] = None type: str = "message" role: str = "system"@dataclassclass UserMessageItemParam: content: List[dict] # Similarly, content can be more specific id: Optional[str] = None status: Optional[str] = None type: str = "message" role: str = "user"@dataclassclass AssistantMessageItemParam: content: List[dict] # Content structure here depends on your schema id: Optional[str] = None status: Optional[str] = None type: str = "message" role: str = "assistant"@dataclassclass FunctionCallItemParam: name: str call_id: str arguments: str type: str = "function_call" id: Optional[str] = None status: Optional[str] = None@dataclassclass FunctionCallOutputItemParam: call_id: str output: str id: Optional[str] = None type: str = "function_call_output"# Union of all possible item typesItemParam = Union[ SystemMessageItemParam, UserMessageItemParam, AssistantMessageItemParam, FunctionCallItemParam, FunctionCallOutputItemParam]# Assuming the EventType and other enums are already defined# For reference:class EventType(str, Enum): SESSION_UPDATE = "session.update" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_APPEND = "input_audio_buffer.append" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_COMMIT = "input_audio_buffer.commit" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_CLEAR = "input_audio_buffer.clear" UPDATE_CONVERSATION_CONFIG = "update_conversation_config" ITEM_CREATE = "conversation.item.create" ITEM_TRUNCATE = "conversation.item.truncate" ITEM_DELETE = "conversation.item.delete" RESPONSE_CREATE = "response.create" RESPONSE_CANCEL = "response.cancel" ERROR = "error" SESSION_CREATED = "session.created" SESSION_UPDATED = "session.updated" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_COMMITTED = "input_audio_buffer.committed" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_CLEARED = "input_audio_buffer.cleared" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_SPEECH_STARTED = "input_audio_buffer.speech_started" INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_SPEECH_STOPPED = "input_audio_buffer.speech_stopped" ITEM_CREATED = "conversation.item.created" ITEM_DELETED = "conversation.item.deleted" ITEM_TRUNCATED = "conversation.item.truncated" ITEM_INPUT_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPTION_COMPLETED = "conversation.item.input_audio_transcription.completed" ITEM_INPUT_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPTION_FAILED = "conversation.item.input_audio_transcription.failed" RESPONSE_CREATED = "response.created" RESPONSE_CANCELLED = "response.cancelled" RESPONSE_DONE = "response.done" RESPONSE_OUTPUT_ITEM_ADDED = "response.output_item.added" RESPONSE_OUTPUT_ITEM_DONE = "response.output_item.done" RESPONSE_CONTENT_PART_ADDED = "response.content_part.added" RESPONSE_CONTENT_PART_DONE = "response.content_part.done" RESPONSE_TEXT_DELTA = "response.text.delta" RESPONSE_TEXT_DONE = "response.text.done" RESPONSE_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPT_DELTA = "response.audio_transcript.delta" RESPONSE_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPT_DONE = "response.audio_transcript.done" RESPONSE_AUDIO_DELTA = "response.audio.delta" RESPONSE_AUDIO_DONE = "response.audio.done" RESPONSE_FUNCTION_CALL_ARGUMENTS_DELTA = "response.function_call_arguments.delta" RESPONSE_FUNCTION_CALL_ARGUMENTS_DONE = "response.function_call_arguments.done" RATE_LIMITS_UPDATED = "rate_limits.updated"# Base class for all ServerToClientMessages@dataclassclass ServerToClientMessage: event_id: str@dataclassclass ErrorMessage(ServerToClientMessage): error: RealtimeError type: str = EventType.ERROR@dataclassclass SessionCreated(ServerToClientMessage): session: Session type: str = EventType.SESSION_CREATED@dataclassclass SessionUpdated(ServerToClientMessage): session: Session type: str = EventType.SESSION_UPDATED@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferCommitted(ServerToClientMessage): item_id: str type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_COMMITTED previous_item_id: Optional[str] = None@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferCleared(ServerToClientMessage): type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_CLEARED@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted(ServerToClientMessage): audio_start_ms: int item_id: str type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_SPEECH_STARTED@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferSpeechStopped(ServerToClientMessage): audio_end_ms: int type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_SPEECH_STOPPED item_id: Optional[str] = None@dataclassclass ItemCreated(ServerToClientMessage): item: ItemParam type: str = EventType.ITEM_CREATED previous_item_id: Optional[str] = None@dataclassclass ItemTruncated(ServerToClientMessage): item_id: str content_index: int audio_end_ms: int type: str = EventType.ITEM_TRUNCATED@dataclassclass ItemDeleted(ServerToClientMessage): item_id: str type: str = EventType.ITEM_DELETED# Assuming the necessary enums, ItemParam, and other classes are defined above# ResponseStatus could be a string or an enum, depending on your schema# Enum or Literal for ResponseStatus (could be more extensive)ResponseStatus = Union[str, Literal["in_progress", "completed", "cancelled", "incomplete", "failed"]]# Define status detail classes@dataclassclass ResponseCancelledDetails: reason: str # e.g., "turn_detected", "client_cancelled" type: str = "cancelled"@dataclassclass ResponseIncompleteDetails: reason: str # e.g., "max_output_tokens", "content_filter" type: str = "incomplete"@dataclassclass ResponseError: type: str # The type of the error, e.g., "validation_error", "server_error" message: str # The error message describing what went wrong code: Optional[str] = None # Optional error code, e.g., HTTP status code, API error code@dataclassclass ResponseFailedDetails: error: ResponseError # Assuming ResponseError is already defined type: str = "failed"# Union of possible status detailsResponseStatusDetails = Union[ResponseCancelledDetails, ResponseIncompleteDetails, ResponseFailedDetails]# Define Usage class to handle token usage@dataclassclass InputTokenDetails: cached_tokens: int text_tokens: int audio_tokens: int@dataclassclass OutputTokenDetails: text_tokens: int audio_tokens: int@dataclassclass Usage: total_tokens: int input_tokens: int output_tokens: int input_token_details: InputTokenDetails output_token_details: OutputTokenDetails# The Response dataclass definition@dataclassclass Response: id: str # Unique ID for the response output: List[ItemParam] = field(default_factory=list) # List of items in the response object: str = "realtime.response" # Fixed value for object type status: ResponseStatus = "in_progress" # Status of the response status_details: Optional[ResponseStatusDetails] = None # Additional details based on status usage: Optional[Usage] = None # Token usage information@dataclassclass ResponseCreated(ServerToClientMessage): response: Response type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_CREATED@dataclassclass ResponseDone(ServerToClientMessage): response: Response type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_DONE@dataclassclass ResponseTextDelta(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int content_index: int delta: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_TEXT_DELTA@dataclassclass ResponseTextDone(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int content_index: int text: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_TEXT_DONE@dataclassclass ResponseAudioTranscriptDelta(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int content_index: int delta: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPT_DELTA@dataclassclass ResponseAudioTranscriptDone(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int content_index: int transcript: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPT_DONE@dataclassclass ResponseAudioDelta(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int content_index: int delta: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_DELTA@dataclassclass ResponseAudioDone(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int content_index: int type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_DONE@dataclassclass ResponseFunctionCallArgumentsDelta(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int call_id: str delta: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_FUNCTION_CALL_ARGUMENTS_DELTA@dataclassclass ResponseFunctionCallArgumentsDone(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str item_id: str output_index: int call_id: str name: str arguments: str type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_FUNCTION_CALL_ARGUMENTS_DONE@dataclassclass RateLimitDetails: name: str # Name of the rate limit, e.g., "api_requests", "message_generation" limit: int # The maximum number of allowed requests in the current time window remaining: int # The number of requests remaining in the current time window reset_seconds: float # The number of seconds until the rate limit resets@dataclassclass RateLimitsUpdated(ServerToClientMessage): rate_limits: List[RateLimitDetails] type: str = EventType.RATE_LIMITS_UPDATED@dataclassclass ResponseOutputItemAdded(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str # The ID of the response output_index: int # Index of the output item in the response item: Union[ItemParam, None] # The added item (can be a message, function call, etc.) type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_OUTPUT_ITEM_ADDED # Fixed event type@dataclassclass ResponseContentPartAdded(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str # The ID of the response item_id: str # The ID of the item to which the content part was added output_index: int # Index of the output item in the response content_index: int # Index of the content part in the output part: Union[ItemParam, None] # The added content part type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_CONTENT_PART_ADDED # Fixed event type@dataclassclass ResponseContentPartDone(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str # The ID of the response item_id: str # The ID of the item to which the content part belongs output_index: int # Index of the output item in the response content_index: int # Index of the content part in the output part: Union[ItemParam, None] # The content part that was completed type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_CONTENT_PART_ADDED # Fixed event type@dataclassclass ResponseOutputItemDone(ServerToClientMessage): response_id: str # The ID of the response output_index: int # Index of the output item in the response item: Union[ItemParam, None] # The output item that was completed type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_OUTPUT_ITEM_DONE # Fixed event type@dataclassclass ItemInputAudioTranscriptionCompleted(ServerToClientMessage): item_id: str # The ID of the item for which transcription was completed content_index: int # Index of the content part that was transcribed transcript: str # The transcribed text type: str = EventType.ITEM_INPUT_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPTION_COMPLETED # Fixed event type@dataclassclass ItemInputAudioTranscriptionFailed(ServerToClientMessage): item_id: str # The ID of the item for which transcription failed content_index: int # Index of the content part that failed to transcribe error: ResponseError # Error details explaining the failure type: str = EventType.ITEM_INPUT_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPTION_FAILED # Fixed event type# Union of all server-to-client message typesServerToClientMessages = Union[ ErrorMessage, SessionCreated, SessionUpdated, InputAudioBufferCommitted, InputAudioBufferCleared, InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted, InputAudioBufferSpeechStopped, ItemCreated, ItemTruncated, ItemDeleted, ResponseCreated, ResponseDone, ResponseTextDelta, ResponseTextDone, ResponseAudioTranscriptDelta, ResponseAudioTranscriptDone, ResponseAudioDelta, ResponseAudioDone, ResponseFunctionCallArgumentsDelta, ResponseFunctionCallArgumentsDone, RateLimitsUpdated, ResponseOutputItemAdded, ResponseContentPartAdded, ResponseContentPartDone, ResponseOutputItemDone, ItemInputAudioTranscriptionCompleted, ItemInputAudioTranscriptionFailed]# Base class for all ClientToServerMessages@dataclassclass ClientToServerMessage: event_id: str = field(default_factory=generate_event_id)@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferAppend(ClientToServerMessage): audio: Optional[str] = field(default=None) type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_APPEND # Default argument (has a default value)@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferCommit(ClientToServerMessage): type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_COMMIT@dataclassclass InputAudioBufferClear(ClientToServerMessage): type: str = EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_CLEAR@dataclassclass ItemCreate(ClientToServerMessage): item: Optional[ItemParam] = field(default=None) # Assuming `ItemParam` is already defined type: str = EventType.ITEM_CREATE previous_item_id: Optional[str] = None@dataclassclass ItemTruncate(ClientToServerMessage): item_id: Optional[str] = field(default=None) content_index: Optional[int] = field(default=None) audio_end_ms: Optional[int] = field(default=None) type: str = EventType.ITEM_TRUNCATE@dataclassclass ItemDelete(ClientToServerMessage): item_id: Optional[str] = field(default=None) type: str = EventType.ITEM_DELETE @dataclassclass ResponseCreateParams: commit: bool = True # Whether the generated messages should be appended to the conversation cancel_previous: bool = True # Whether to cancel the previous pending generation append_input_items: Optional[List[ItemParam]] = None # Messages to append before response generation input_items: Optional[List[ItemParam]] = None # Initial messages to use for generation modalities: Optional[Set[str]] = None # Allowed modalities (e.g., "text", "audio") instructions: Optional[str] = None # Instructions or guidance for the model voice: Optional[Voices] = None # Voice setting for audio output output_audio_format: Optional[AudioFormats] = None # Format for the audio output tools: Optional[List[Dict[str, Any]]] = None # Tools available for this response tool_choice: Optional[ToolChoice] = None # How to choose the tool ("auto", "required", etc.) temperature: Optional[float] = None # The randomness of the model's responses max_response_output_tokens: Optional[Union[int, str]] = None # Max number of tokens for the output, "inf" for infinite@dataclassclass ResponseCreate(ClientToServerMessage): type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_CREATE response: Optional[ResponseCreateParams] = None # Assuming `ResponseCreateParams` is defined@dataclassclass ResponseCancel(ClientToServerMessage): type: str = EventType.RESPONSE_CANCELDEFAULT_CONVERSATION = "default"@dataclassclass UpdateConversationConfig(ClientToServerMessage): type: str = EventType.UPDATE_CONVERSATION_CONFIG label: str = DEFAULT_CONVERSATION subscribe_to_user_audio: Optional[bool] = None voice: Optional[Voices] = None system_message: Optional[str] = None temperature: Optional[float] = None max_tokens: Optional[int] = None tools: Optional[List[dict]] = None tool_choice: Optional[ToolChoice] = None disable_audio: Optional[bool] = None output_audio_format: Optional[AudioFormats] = None@dataclassclass SessionUpdate(ClientToServerMessage): session: Optional[SessionUpdateParams] = field(default=None) # Assuming `SessionUpdateParams` is defined type: str = EventType.SESSION_UPDATE# Union of all client-to-server message typesClientToServerMessages = Union[ InputAudioBufferAppend, InputAudioBufferCommit, InputAudioBufferClear, ItemCreate, ItemTruncate, ItemDelete, ResponseCreate, ResponseCancel, UpdateConversationConfig, SessionUpdate]def from_dict(data_class, data): """Recursively convert a dictionary to a dataclass instance.""" if is_dataclass(data_class): # Check if the target class is a dataclass fieldtypes = {f.name: f.type for f in data_class.__dataclass_fields__.values()} return data_class(**{f: from_dict(fieldtypes[f], data[f]) for f in data}) elif isinstance(data, list): # Handle lists of nested dataclass objects return [from_dict(data_class.__args__[0], item) for item in data] else: # For primitive types (str, int, float, etc.), return the value as-is return datadef parse_client_message(unparsed_string: str) -> ClientToServerMessage: data = json.loads(unparsed_string) # Dynamically select the correct message class based on the `type` field, using from_dict if data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_APPEND: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferAppend, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_COMMIT: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferCommit, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_CLEAR: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferClear, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_CREATE: return from_dict(ItemCreate, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_TRUNCATE: return from_dict(ItemTruncate, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_DELETE: return from_dict(ItemDelete, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_CREATE: return from_dict(ResponseCreate, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_CANCEL: return from_dict(ResponseCancel, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.UPDATE_CONVERSATION_CONFIG: return from_dict(UpdateConversationConfig, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.SESSION_UPDATE: return from_dict(SessionUpdate, data) raise ValueError(f"Unknown message type: {data['type']}")# Assuming all necessary classes and enums (EventType, ServerToClientMessages, etc.) are imported# Here’s how you can dynamically parse a server-to-client message based on the `type` field:def parse_server_message(unparsed_string: str) -> ServerToClientMessage: data = json.loads(unparsed_string) # Dynamically select the correct message class based on the `type` field, using from_dict if data["type"] == EventType.ERROR: return from_dict(ErrorMessage, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.SESSION_CREATED: return from_dict(SessionCreated, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.SESSION_UPDATED: return from_dict(SessionUpdated, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_COMMITTED: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferCommitted, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_CLEARED: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferCleared, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_SPEECH_STARTED: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferSpeechStarted, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.INPUT_AUDIO_BUFFER_SPEECH_STOPPED: return from_dict(InputAudioBufferSpeechStopped, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_CREATED: return from_dict(ItemCreated, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_TRUNCATED: return from_dict(ItemTruncated, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_DELETED: return from_dict(ItemDeleted, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_CREATED: return from_dict(ResponseCreated, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_TEXT_DELTA: return from_dict(ResponseTextDelta, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_TEXT_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseTextDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPT_DELTA: return from_dict(ResponseAudioTranscriptDelta, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPT_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseAudioTranscriptDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_DELTA: return from_dict(ResponseAudioDelta, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_AUDIO_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseAudioDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_FUNCTION_CALL_ARGUMENTS_DELTA: return from_dict(ResponseFunctionCallArgumentsDelta, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_FUNCTION_CALL_ARGUMENTS_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseFunctionCallArgumentsDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RATE_LIMITS_UPDATED: return from_dict(RateLimitsUpdated, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_OUTPUT_ITEM_ADDED: return from_dict(ResponseOutputItemAdded, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_CONTENT_PART_ADDED: return from_dict(ResponseContentPartAdded, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_CONTENT_PART_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseContentPartDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.RESPONSE_OUTPUT_ITEM_DONE: return from_dict(ResponseOutputItemDone, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_INPUT_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPTION_COMPLETED: return from_dict(ItemInputAudioTranscriptionCompleted, data) elif data["type"] == EventType.ITEM_INPUT_AUDIO_TRANSCRIPTION_FAILED: return from_dict(ItemInputAudioTranscriptionFailed, data) raise ValueError(f"Unknown message type: {data['type']}") def to_json(obj: Union[ClientToServerMessage, ServerToClientMessage]) -> str: return json.dumps(asdict(obj))The agent.py imports key classes from rtc.py, which implements the server-side Agora Python Voice SDK, facilitating communication and managing audio streams.
Test the Code
Setup and run the backend
To set up and run the backend, take the following steps:
-
Make sure that you have updated the files in the
realtime_agentfolder with the complete code. -
Update the values for
AGORA_APP_ID,AGORA_APP_CERT, andOPENAI_API_KEYin the project's.envfile.Ensure that the necessary credentials for Agora and OpenAI are correctly configured.
-
Execute the following command to run the demo agent:
Replace
<channel_name>with the desired channel name and<agent_uid>with a unique user ID.
Start HTTP server
To start the HTTP server:
The server provides a simple layer for managing agent processes.
POST /start_agent
This api starts an agent with given graph and override properties. The started agent joins the specified channel, and subscribes to the uid which your browser/device's rtc used to join.
| Param | Description |
|---|---|
channel_name (string) | Use the same channel name that your browser/device joins, agent needs to be in the same channel to communicate. |
uid (unsigned int) | The user ID that the AI agent uses to join. |
Example:
POST /stop_agent
This api stops the agent you started.
| Param | Description |
|---|---|
channel_name (string) | Use the same channel name you used to start the agent. |
Example:
Front-end for testing
Use Agora's Voice Call Demo for testing. Join with your AppID and generate a token from the project settings page on the Agora Console.
Reference
Additional relevant documentation that complements the current page or explains other aspects of the product.